If you have been diagnosed with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) and you need to begin dialysis, you will need to have an access placed. If hemodialysis is needed immediately, the only option that allows for immediate use after placement is a central venous catheter (CVC). The United States Renal Data System’s 2015 report stated that 80% of ESRD patients began dialysis with a central venous catheter.
What is a Central Venous Catheter?
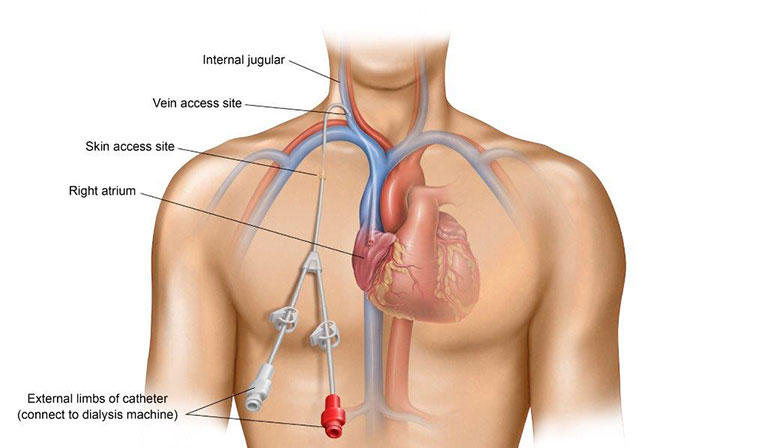
A central venous catheter (CVC) is a type of access used for hemodialysis. Tunneled CVCs are placed under the skin and into a large central vein, preferably the internal jugular veins. CVCs are meant to be used for a short period of time until a more permanent type of dialysis access has been established.
Tunneled CVC’s are placed under the skin and meant to be used for a longer duration of time versus non-tunneled, which are designed to be temporary.
What is the Procedure for Central Venous Catheter Placement?
This procedure is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed in an outpatient setting. The central venous catheter placement procedure begins with your physician administering local anesthesia to numb the selected area for catheter insertion. Ultrasound may be used to determine the exact site on the body where the catheter will be placed. Fluoroscopy, a type of x-ray, may be used to further guide the catheter through the skin, and into the selected central vein. The catheter is advanced into the central vein until the tip of the CVC reaches the right atrium. There are small cuffs on the catheter that lay just under the skin that aid in keeping the catheter properly placed and minimize the risk of infection.
Recovering from Central Venous Catheter Placement
After the central venous catheter placement procedure, there may be some pain and swelling around your insertion site. If you need to start dialysis treatment immediately, your CVC is ready for use. If you do not have to start dialysis immediately and have had the catheter placed in an outpatient setting, you will be able to go home at the end of the procedure.
Central Venous Catheter Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Dialysis can be performed immediately
- Readily inserted during an outpatient procedure
- Easy placement and removal
- Avoids extra needle sticks
Cons:
- Not ideal for use as a permanent access
- High infection rates
- Difficult to obtain sufficient blood flow to allow for adequate toxin removal
- May cause narrowed veins
- Swimming and bathing is not recommended
How We Can Help You
Our vascular specialists are highly skilled at placing CVCs for dialysis in the outpatient setting as well as the ongoing care and management of your dialysis access. At Azura Vascular Care, we work every day to deliver far more than our patients expect. We bring our full range of medical capabilities and service excellence to every patient, every visit at each of our centers nationwide.
If you would like to learn more about a specific medical condition leading to dialysis, or about dialysis itself, Fresenius Kidney Care is a complete resource for CKD .
If you are ready to consult with one of our specialists, find a center near you or search for one of our physicians.
Ready to Speak with a Specialist?
Search for a center or physician in your area and request an appointment online.